[Spring] @RestController와 @ResponseBody
Spring에서 컨트롤러를 지정해주는 어노테이션으로 @Controller와 @RestController를 이용합니다. 객체를 Json형태의 데이터로 보내주기 위해서는 컨트롤러의 각 메소드에 @ResponseBody 어노테이션을 붙여주는데요, 며칠전 프로젝트를 진행하며 컨트롤러에 붙은 어노테이션을 확인하다 동료가 컨트롤러에 @RestController와 @ResponseBody를 함께 사용한 것을 확인했습니다. @RestController 어노테이션을 뜯어보면 @ResponseBody가 들어있는 것을 확인할 수 있는데요, 그렇다면 @RestController를 사용한 컨트롤러에서는 메소드에 @ResponseBody를 사용하지 않아도 되는 걸까요?
당연히 그렇습니다. 그럼 @ResponseBody와 @RestController는 어떤 방식으로 작동할까요
@Controller로 View를 반환
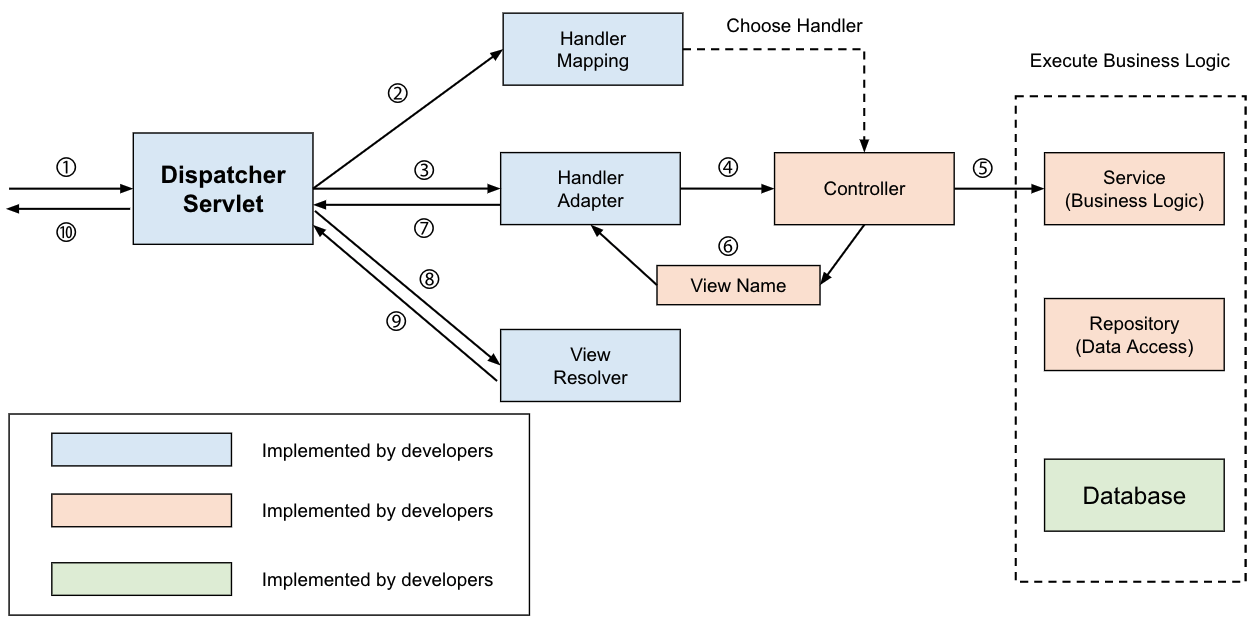
서버에서 view까지 모두 관리하던 전통적인 Spring MVC(혹은 MTV)에서는 @Controller가 view를 반환하기 위해 사용되었습니다. Thymleaf 등의 템플릿 엔진 등을 이용해보면 컨트롤러(@Controller가 붙어있는)에서 model에 데이터를 담아 view 파일의 이름을 반환합니다. 일반적으로 View를 반환하는 컨트롤러는 다음과 같이 작동하게 됩니다.
- 클라이언트가 URI 형식으로 웹 서비스에 요청을 보낸다.
- Dispatcher Servlet이 요청을 위임할 HandlerMapping을 찾는다.
- HandlerMapping을 통해 요청을 Controller로 위임한다.
- Controller는 요청을 처리한 후에 ViewName을 반환한다.
- DispatcherServlet은 ViewResolver를 통해 ViewName에 해당하는 view를 찾아 사용자에게 반환한다.
@Controller로 Data를 반환
클라이언트와 서버가 분리되어 서로 Json 형태의 데이터를 주고 받는 현대의 통신방식에서는 컨트롤러에서는 view가 아니라 객체를 Json 형태의 데이터로 변환하여 반환할 필요가 있습니다. 이때 @ResponseBody를 메소드에 붙여주는데요, @ResponseBody가 붙은 메소드에서 Spring은 반환값을 변환하여 HTTP Response의 Body에 자동으로 값을 입력해줍니다.
컨트롤러를 통해 객체를 반환할 때에는 일반적으로 ResponseEntity로 감싸서 반환을 합니다. 보내는 응답의 헤더와 상태코드를 직접 다루기 위해서인데요, ResponseEntity를 Json으로 변환하기 위해 @ResponseBody를 사용합니다.
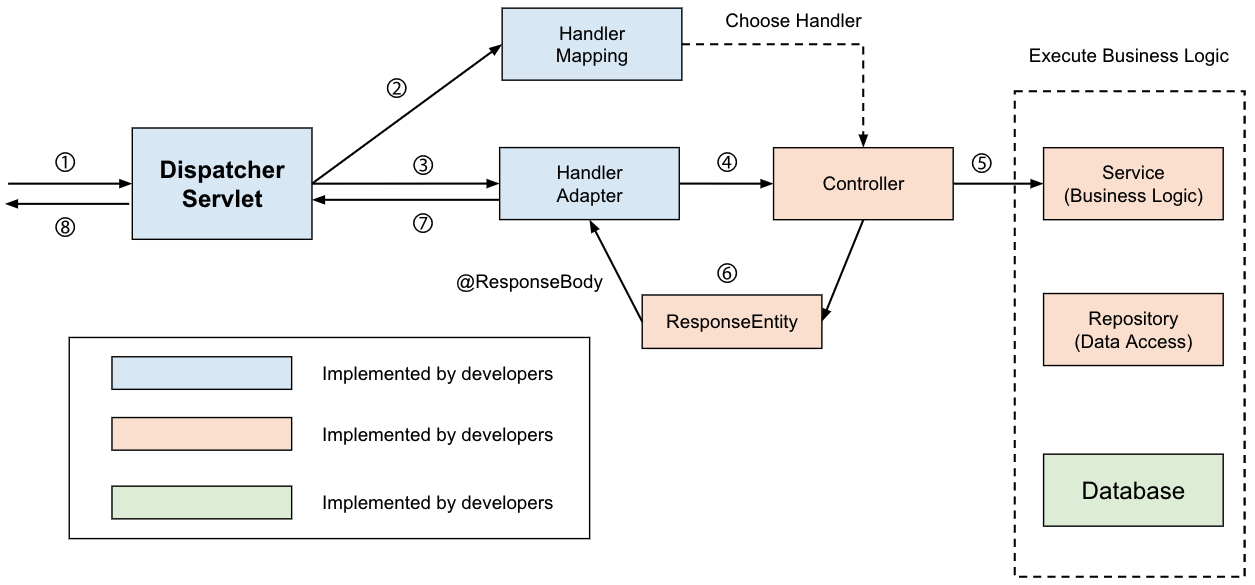
더불어 객체를 반환할 때에는 viewResolver 대신 HttpMessageConverter가 동작합니다. HttpMessageConverter에는 여러가지 Converter가 등록되어 있고, 반환해야하는 데이터에 따라 사용되는 Converter가 달라집니다. (ex. String -> StringHttpMessageConverter, 객체 -> MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter) MessageConverter는 HandlerAdapter와 Controller가 요청을 주고 받는 시점에 동작합니다.
RestController
@RestController는 @Controller에 @ResponseBody가 추가된 것입니다. @RestController가 붙은 컨트롤러의 메소드는 REST API 주로 사용하는 현대의 요청/응답 통신에서 많이 사용되며, 객체를 ResponseEntity로 감싸서 반환합니다. 동작 방식 역시 @Controller에 @ResponseBody를 붙인 것과 동일합니다.

객체를 ResponseEntity로 감싸서 반환해주는 이유는 @RestController가 붙은 컨트롤러의 메소드에서 객체만을 반환할 경우, HttpStatus를 설정해줄 수 없기 때문입니다. 객체 생성(201 CREATED) 등에 관한 상태 메시지와 코드를 반환해줄 수 없다는 문제가 발생하기 때문에 객체를 상황에 맞게 ResponseEntity로 감싸서 반환해주어야 합니다.
package org.springframework.web.bind.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
/**
* A convenience annotation that is itself annotated with
* {@link Controller @Controller} and {@link ResponseBody @ResponseBody}.
* <p>
* Types that carry this annotation are treated as controllers where
* {@link RequestMapping @RequestMapping} methods assume
* {@link ResponseBody @ResponseBody} semantics by default.
*
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> {@code @RestController} is processed if an appropriate
* {@code HandlerMapping}-{@code HandlerAdapter} pair is configured such as the
* {@code RequestMappingHandlerMapping}-{@code RequestMappingHandlerAdapter}
* pair which are the default in the MVC Java config and the MVC namespace.
*
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @author Sam Brannen
* @since 4.0
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public @interface RestController {
/**
* The value may indicate a suggestion for a logical component name,
* to be turned into a Spring bean in case of an autodetected component.
* @return the suggested component name, if any (or empty String otherwise)
* @since 4.0.1
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = Controller.class)
String value() default "";
}
@RestController의 내부를 보면 @ResponseBody를 가지고 있는 것을 알 수 있습니다. 따라서 Json/xml 형태의 데이터를 통해 통신하기 위해서 @RestController를 사용할 때에는 컨트롤러에 있는 각 메소드에 @ResponseBody를 붙이는 작업을 하지 않아도 붙인 것과 동일하게 작동합니다.
참고
- https://dev-coco.tistory.com/99
- https://mangkyu.tistory.com/49
- https://highcode.tistory.com/24